How do Flagship Smartphones Generate More Revenue for Smartphone Manufacturers Despite Selling Fewer Units?
In the dynamic world of smartphones, two categories often dominate the conversation: Flagship devices and Mid-range devices. Flagships, with their cutting-edge technology and premium price tags, command attention as the pinnacle of smartphone innovation. Mid-range smartphones, on the other hand, cater to a wider audience by offering a balance between performance and affordability. While mid-range devices offer impressive value for money, they often fall short of delivering the comprehensive, high-end experience found in flagship models.
Flagships with their headlines making impressive features, demand high prices. While it may seem counterintuitive but flagships, despite selling fewer units, often generate more revenue for smartphone manufacturers. It’s essential to recognize that revenue generation doesn’t always align with sales volume. Here, we delve into why flagship smartphones, despite selling fewer units, often generate more revenue for manufacturers.
Some Data Insights
Top 5 smartphone companies based on their revenue
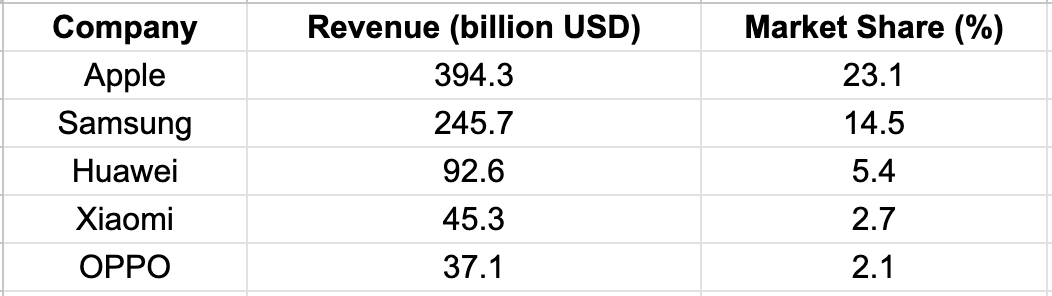
Most Sold Samsung Devices
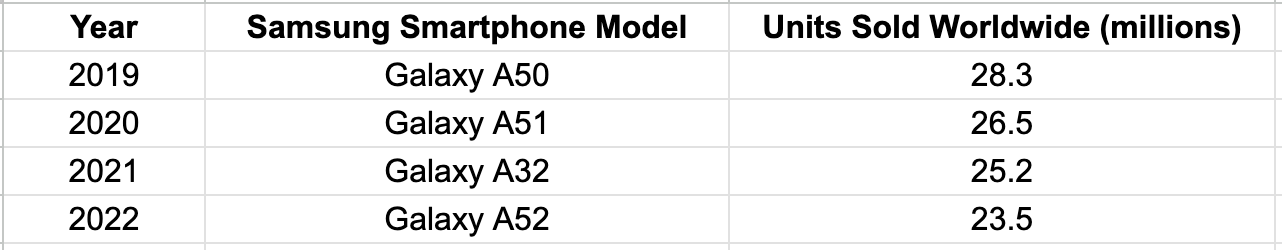
Most Sold Samsung Flagship Devices
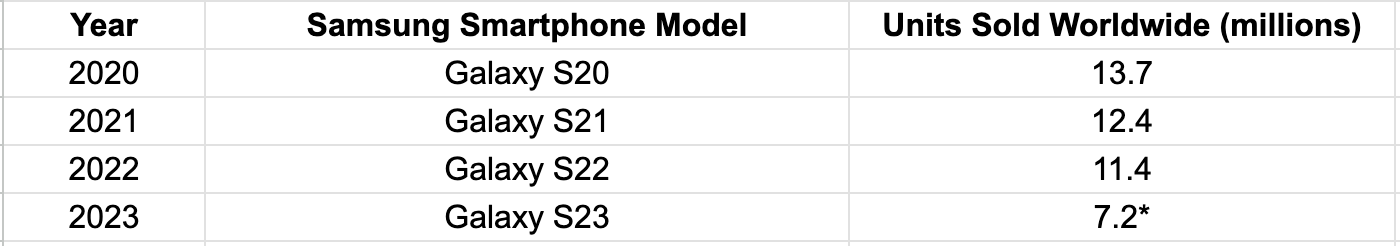
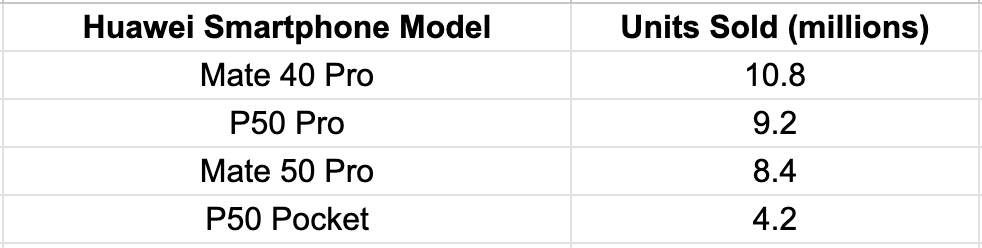
Most Sold Huawei Devices
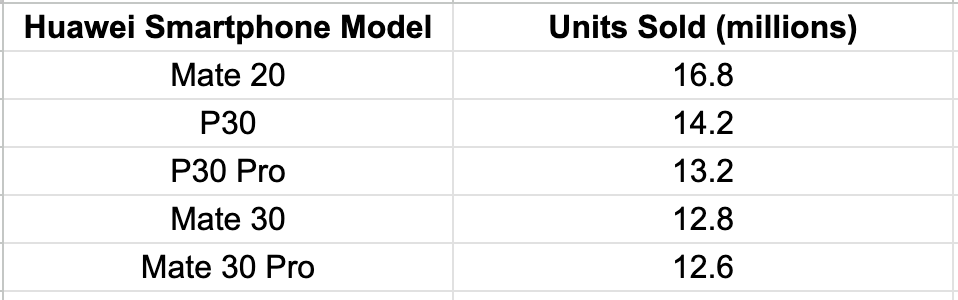
Most Sold Huawei Flagship Devices
Higher Profit Margins for Flagship Devices
Flagship smartphones are known for their premium features and innovative functionalities. These devices represent the manufacturer’s ingenious capabilities. They incorporate the latest technology, from top-tier processors to advanced camera systems and high-resolution displays. Flagship smartphones, with their cutting-edge technology and premium features, command significantly higher prices than mid-range devices.
While this may deter some potential buyers, it translates into larger profit margins for manufacturers. Even with fewer units sold, the substantial profit per unit compensates for the lower sales volume, translating into substantial revenues. This profit cushion enables smartphone companies to invest more in research and development, further enhancing the quality and innovation of their flagship offerings. Consequently, flagship devices remain a lucrative venture for smartphone companies.
Also read: Smartphone Evolution: Exploring the Saturation Point
Higher Competition in Mid-Range Devices
The low and mid-range smartphone market is a fiercely competitive battleground. Manufacturers grapple with the challenge of delivering a flagship-like experience within a budget-conscious price range. This task is far from simple, as cost-cutting measures must be implemented judiciously to avoid compromising the user experience. Striking the delicate balance between user-affordability and user satisfaction is imperative to prevent any compromise to the brand identity. This intensified competition and the need to maintain a plausible cost-to-quality ratio restrict profit margins for mid-range smartphones. Achieving this equilibrium often means operating with very thin profit margins.
However, in flagship world, profitability thrives on fewer units commanding higher prices and yielding more substantial profit margins. As a result, the mid-range smartphone market necessitates a high volume of sales to match the revenue generated by their flagship counterparts.
Bloatware Conundrum and User Experience
A contentious issue often associated with mid-range smartphones is bloatware — pre-installed applications and software that cannot be readily removed by users. This bloatware often becomes necessary to be included in the mid-range devices for compensating the lower price along with flagship-like features.

This unwanted software can blemish the user experience, particularly in premier smartphone markets like Europe and the United States, where consumers prioritize a seamless, bloatware-free software environment. This readiness to spend more on flagship devices for a better user-experience, directly contributes to bolstering the overall revenue of smartphone manufacturers from these markets. Moreover, since smartphone markets like Europe and US have an affluent user-base, the users aren’t reluctant to pay exorbitant amount of money to buy latest flagship models and their accessories. And this results in generating even more revenue for the smartphone companies from their higher-end models.
User Base and Upgrade Patterns
Mid-range smartphones cater to a user base with some particular characteristics. A significant portion of the mid-range smartphone market comprises users who face budget constraints. These consumers are often budget-conscious and seek value-oriented options. They typically refrain from upgrading their devices until they become obsolete or cease to function properly. Moreover, because of excessive competition in mid-range segment, smartphone companies fail to retain their users and are unable to create a loyal user-base for their next generation mid-range devices. Consequently, mid-range smartphone sales are characterized by more extended replacement cycles .
In contrast, the flagship power user base exhibits different behavior. These users are drawn to flagship smartphones and are more inclined to upgrade regularly from the same company. The allure of new features, improved performance, and the prestige associated with owning the latest flagship model motivates this demographic. Additionally, flagship smartphones tend to retain their value better than mid-range devices, making them appealing options for resale. This characteristic encourages loyal fans to purchase the latest flagship more frequently, further boosting annual-earnings of flagship makers.
Also read: Analyzing the Evolving Landscape of Web Browsers and the Impact of AI
Brand Image and Perception
Flagship smartphones extend beyond their physical attributes; they serve as symbols of status and prestige. Consumers associate flagship devices with innovation, quality, and luxury. This perception allows manufacturers to command higher prices, compelled by the perceived value of owning a flagship smartphone. The association of a particular brand with a status symbol not only justifies the higher price tags but also drives sales among consumers who prioritize these attributes.
Furthermore, the positive brand association cultivated by flagship models has a ripple effect across a manufacturer’s product portfolio. When consumers invest in a flagship device, they become more susceptible to seek other products of the same manufacturer. This interconnectedness drives sales in different price segments and further augments revenue.
Upselling and Cross-selling Opportunities
Flagship smartphones often serve as the entry point into a manufacturer’s ecosystem. These flagships are gateways to the comprehensive ecosystems, cleverly-created by the smartphone makers. Companies leverage this by upselling and cross-selling complementary products and services.
When consumers invest in a flagship device, they often become more inclined to explore and adopt other offerings from the same brand. This creates a cascading effect of increased sales and revenue diversification, further strengthening the manufacturer’s financial position.
In conclusion, the smartphone industry’s revenue landscape is a complex interplay of pricing, competition, user behavior, brand image, and cross-selling opportunities. While mid-range smartphones may dominate in unit sales, flagship devices consistently shine when it comes to generating revenue. Flagships’ higher profit margins, premium perception, and ecosystem integrations create a financial collaboration that mid-range devices often struggle to match. Albeit, mid-range smartphones cater to a broader consumer base, the challenges of thin profit margins and stiff competition hinder their ability to match the revenue-generating prowess of flagship counterparts.
Understanding these nuances within the smartphone industry is crucial for manufacturers seeking to navigate this competitive landscape effectively and sustain financial success. As smartphone manufacturers navigate this ever-competitive terrain, these dynamics will remain pivotal for achieving financial success and industry dominance.